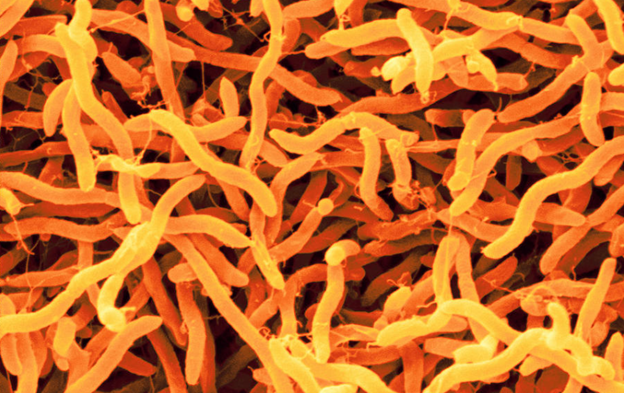
Acrobacter spp., a lesser-known genus of bacteria, has increasingly become a focus of public health concern in North America due to its prevalence in water and food sources. This blog post aims to shed light on the significance of Acrobacter, its health implications, and the challenges it poses to public health in North America.
Understanding Acrobacter spp.
Acrobacter spp. encompasses a group of Gram-negative bacteria that are found in a variety of environments, including water, soil, and food products. While not as notorious as other foodborne pathogens like Salmonella or E. coli, Acrobacter spp. has been identified as a cause of gastroenteritis, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems.
Prevalence in North America
The prevalence of Acrobacter in North America has been subject to increased scrutiny. Studies have identified these bacteria in drinking water, fresh produce, and meat products, underscoring their widespread presence. The exact prevalence rates can vary, but detections in water systems and food samples indicate a relatively common occurrence.
Health Burden and Risks
The health burden associated with Acrobacter spp. in North America, while not as high as more well-known pathogens, is nonetheless significant. Infections can lead to symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to more severe gastrointestinal distress, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, infants, and those with weakened immune systems. The risk is compounded by the bacteria's ability to form biofilms, making it resistant to standard disinfection methods used in water treatment and food processing.
Challenges in Detection and Control
One of the primary challenges in managing the risk associated with Acrobacter spp. is detection. Traditional microbial testing methods may not always effectively identify these bacteria, leading to underreporting and a lack of awareness about their presence in the food supply and water sources. Furthermore, the bacteria's resilience and adaptability to various environments make it a challenging pathogen to control.
Efforts to Mitigate the Risk
Efforts to mitigate the risk of Acrobacter infections in North America include enhancing surveillance and detection methods, implementing stricter guidelines for water treatment and food safety, and conducting research to better understand the bacteria's behavior and resistance mechanisms. Public health campaigns focusing on proper food handling and preparation practices also play a critical role in reducing exposure.
The Way Forward
Addressing the challenges posed by Acrobacter spp. requires a coordinated effort among public health officials, water and food industry stakeholders, and the research community. By improving detection methods, enforcing rigorous safety standards, and raising public awareness, the burden of Acrobacter-related illnesses can be minimized.
Conclusion
While Acrobacter spp. may not dominate headlines like other pathogens, its prevalence in North America and associated health risks highlight the need for ongoing vigilance in water and food safety practices. As we continue to understand more about these bacteria, targeted strategies to protect public health can be developed and implemented, ensuring the safety of our water and food sources.
